[ad_1]
Happy Friday, everyone, and welcome back to This Week in Space: the best little space news column in Texas. Let’s jump right in.
Private Aerospace Startup to Launch Europe’s First Reusable Rocket
PLD Space, a Spanish aerospace startup, says it’s on track to launch its reusable rocket Miura-1 as early as this summer. If successful, the launch will represent two achievements: This would be the first reusable rocket of European design and Spain’s first privately developed rocket.
Miura-1 (above) is a single-stage, suborbital keralox rocket, which will launch from PLD Space’s facility at Médano del Loro, a stretch of open, sandy beach on the Atlantic Coast of Spain. The company had attempted a launch on May 31, but high winds scrubbed the countdown.
“We plan to launch in the following days/weeks, weather permitting,” said Francesc Casas of PLD Space. However, he added, there won’t be much warning when the launch window opens: “We will not be able to know when we launch until 24 hours prior.”
Scientists Beam Solar Power Down From Space
Space-based solar power has appeared in science fiction for the better part of a century. The California Institute of Technology’s Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1) was launched in January to turn science fiction into science fact. The project team has successfully detected SSPD-1’s microwave power transmission, proving that space-based solar can at least theoretically work.
“Through the experiments we have run so far, we received confirmation that MAPLE [Microwave Array for Power-transfer Low-orbit Experiment] can transmit power successfully to receivers in space,” Dr. Ali Hajimiri, Co-Director of the Space-Based Solar Power Project, said in a statement. “We have also been able to program the array to direct its energy toward Earth, which we detected here at Caltech. We had, of course, tested it on Earth, but now we know that it can survive the trip to space and operate there.”
Whether space-based solar power makes any sense to deploy is still a question scientists are hashing out. The advantages are significant: It’s always solar noon in space, and there’s no atmosphere to get in the way. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind require grid backup because these solutions have a relatively low capacity factor. In space, the Sun is literally always shining, and solar’s capacity factor is virtually 100 percent. So far, so good.
The problems, however, are formidable. Satellite launch costs are expensive, and the land requirements for the ground receiving stations would be enormous. Service missions to any satellites would be limited, and the cost of repairing broken equipment would dwarf the same replacement cost on Earth. There are also energy losses to consider during the conversion from photons to microwaves and back to photons. Companies like SpaceX have been driving launch costs lower, which helps, but that’s only one problem among many that must be resolved. Scientific firsts are scientific firsts, so congratulations to the Caltech team on a lot of hard work.
ESA Announces Indefinite Delay for Final Ariane 5 Flight
Today was supposed to be the last flight of the Ariane 5, Arianespace’s heavy launch vehicle and workhorse of the ESA. However, Arianespace announced yesterday (Thursday) that the launch was delayed indefinitely due to a risk to “the redundancy of a critical function on the Ariane 5.”
During a short call on Thursday, the company stated it detected a problem in the Ariane 5’s pyrotechnical transmission lines during acceptance testing for a different program. Arianespace X-rayed the same lines attached to this specific Ariane 5 and found potential flaws in three lines: two in the rocket booster separation system and one in the distancing system. A further investigation on June 14 and June 15 indicated more problems than the company was comfortable with.
“Because these tests were not all successful, and therefore were not able to give us sufficient confidence on the reliability of the redundancies, it was decided not to go in flight and to replace these doubtful lines,” said Pierre-Yves Tissier, Arianespace’s Chief Technical Officer.
Ariane 5 has multiple redundant systems and could theoretically have launched, but Arianespace’s policy is only to launch when the rocket’s redundant and primary systems are fully cleared. The Ariane 5 has been a reliable workhorse for decades, and nobody wants to see the rocket’s last launch end in failure. The gap between the Ariane 5 and Ariane 6 is supposed to be short, with the new rocket taking its first flight in 2024. That said, Ariane 6 is already years behind schedule, and a further delay wouldn’t be surprising.
ESA Delivers European Service Module for Artemis II
Speaking of gigantic, delayed spacecraft with limited shelf lives, this week, the ESA also formally transferred into US custody the European Service Module (ESM-2) that will fly with Artemis II. The module will attach to the Orion crew capsule and provide air, water, and propulsion for the duration of the flight.
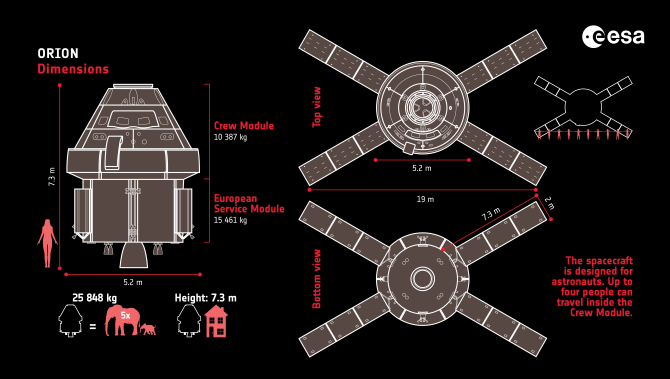
Credit: ESA
“The handover is a formality, but it is an important milestone for the program. It could not have been achieved without the tremendous effort of all the teams involved,” said ESA’s European Service Module production manager Anthony Thirkettle, during a handover ceremony at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. “ESA will continue to work closely with our NASA and industry colleagues on getting the Orion spacecraft ready for launch and throughout the Artemis II mission.”
Chris Hadfield, King Charles III to Pen ‘Astra Carta’
Chris Hadfield has partnered with King Charles III on a space sustainability plan called the Astra Carta, to be released later this summer. (The name is a nod to the Magna Carta, a piece of English legislation from 1215 that has since come to underpin many democracies.) The plan would lay out guidelines for how spacefaring nations should behave on the Moon.
“What would we do with it? Who would own it? Whose laws? Who can drill and who can take advantage of the short-term and long-term resources that exist there,” Hadfield asked in an interview with the Canadian Press. “And how are we going to self-govern? If you kill somebody on the Moon, whose court are you appearing in?”
Humanity has a new opportunity to define ourselves and our values as nations as we slip the surly bonds of Earth. As we venture further into space, facing unimagined hazards and making our mark on the soil of other worlds in far more ways than bootprints—what kind of people do we want to be? “How we settle the Moon,” said Hadfield, “is how we’re going to settle every place we go after.”
Hadfield has been working on the project with King Charles since last summer, when the monarch, who has long espoused environmentalist values, reached out to Hadfield to start the conversation. They plan to release a version of the Astra Carta on June 28 in London.
Curiosity Sends Home ‘Postcard’ From Mars
More than a decade after landing on Mars, the Curiosity rover is still going strong. Right now, it’s on its way out of a region called the Marker Band Valley, exploring the foothills around Mount Sharp. And to commemorate the occasion, NASA released a “postcard” featuring side-by-side images of the same place on Mars, taken in the morning and during its afternoon ‘golden hour.’

Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
For more on the postcard, including the annotated version, click here.
USGS Releases Huge Tranche of Images, Maps of Mars
In recent weeks, there has been a blizzard of new maps of Mars, from space agencies from Canada to China to the ESA. Not to be left behind, the USGS has released a massive trove of thousands of digital terrain models (DTMs) and more than 150,000 high-res images of the Red Planet derived from data gathered by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The team that produced the maps and images had to first carefully align the images to low-res topo maps to get a good read on altitude. But this kind of data processing would have taken years on a regular PC. Thankfully, the USGS has its own supercomputer: the Denali system, boasting some 9,280 cores that can throughput a collective 660 Tflop/s.
Astronomers Find Gas Giant Orbiting 2 Suns
This week, astronomers announced the discovery of a planet resembling Tatooine—at least, inasmuch as that claim can be applied to the planet’s binary suns as opposed to the planet itself. The newly detected world, BEBOP-1c, is thought to be a gas giant roughly 65x more massive than Earth and about 1/5 of Jupiter’s mass. The sky might look like Tatooine’s, but happily, Anakin need not worry about inevitably chaotic distributions of fine-grained sediments.
Most exoplanets have been found by watching for dips in a star’s light output as otherwise-invisible exoplanets orbit between Earth and whatever distant Sun we observe. In this case, the team that found BEBOP-1c used the older radial velocity method. As my colleague Ryan Whitwam discussed earlier this week, the radial velocity method is how scientists identified the first exoplanets. This method involves observing small wobbles in a star’s spectral signature (the degree to which the light is red-shifted or blue-shifted relative to ourselves). Calculating how the light shifts can work well for detecting large exoplanets, and this method works when a star’s planets are not orbiting edge-on as viewed from Earth.
We already know that the companion star to BEBOP-1, TOI-1338, has a planet of its own, TOI-1338b. That planet was detected via the transit method, so scientists know its size but not its mass (radial velocity measurements track minimum mass while transit gives us information on size). The team hopes to combine data from TOI-1338b observations and recover some additional information on BEBOP-1. Even after decades of looking for exoplanets, scientists have only detected a handful compared with more than 2,600 overall. Binary stars are thought to be common in the Milky Way, so understanding more about the characteristics of these planets fills in valuable information on what sorts of worlds are likely to form around various types of stars.
‘A Big, Hot, Strange World’: Atmosphere of Already Inhospitable ‘Hot Jupiter’ Full of Minerals Found in Rock
Scientists looking through the Gemini-North telescope toward the constellation Pisces have made a detailed study of a ‘hot Jupiter’ exoplanet like no other: WASP 76 b. Spectral readings from the gas giant’s surface suggest that the planet’s atmosphere is literally hot enough to vaporize elements typically found in rock.
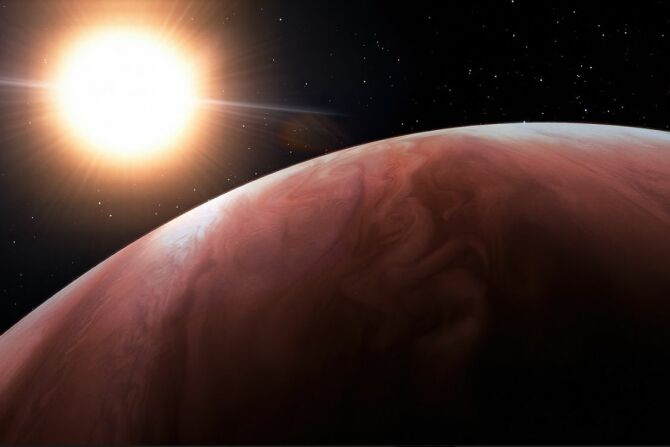

Credit: INTERNATIONAL GEMINI OBSERVATORY/NOIRLAB/NSF/AURA/J. DA SILVA/SPACEENGINE/M. ZAMANI
WASP 76 b orbits a host star much like our own Sun, but that’s where the similarities seem to end. The planet’s surface reaches an incandescent 2,000°C, and it orbits at just a fraction of the distance between Mercury and our Sun. A few years ago, scientists looking at the planet’s Hadean surface temperatures concluded that molten iron would condense out of the planet’s sun-side sky and fall on the far side like a terrible iron rain. And if you remember the Ideal Gas Law from school (yeah, I know, back when rocks were soft), you may remember that if you heat a given substance, it tends to expand. WASP 76 b is comparable to Jupiter in mass but has “puffed up” to six times Jupiter’s volume.
We’re used to hearing about atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and CO₂. But on WASP 76 b, the atmosphere is laden with many elements that make up the crust of our rocky planet: manganese, chromium, magnesium, vanadium, barium, and calcium. WASP 76 b’s atmosphere closely resembles its host star’s, but a few things are missing. Namely, the ones that don’t vaporize until it gets even hotter.
“[The] elements that appear to be missing in WASP-76 b’s atmosphere are precisely those that require higher temperatures to vaporize, like titanium and aluminum,” said study lead Stefan Pelletier, of the University of Montreal, in a statement. “Meanwhile, the ones that matched our predictions, like manganese, vanadium, or calcium, all vaporize at slightly lower temperatures.” The work suggests that similar planets with only slight temperature differences could have vastly different chemistries.
Speed Force: Gaia Survey Finds Half-Dozen Stars Fleeing the Milky Way
On very long time scales, everything in the Milky Way orbits the supermassive black hole at its center. Until this summer, there were only 10 stars in our galaxy whose speed and vector would let them escape the Milky Way. However, a new study of data from the ESA’s Gaia survey has discovered six more runaway stars bound for the big empty.
Two of the speedsters break the record for the fastest radial velocity of any rogue star ever seen: 1694 km/s and 2285 km/s. (For perspective, the velocity of satellites traveling fast enough to stay in LEO is about 8 km/s or 17,000 mph. These stars are moving between 200 and 300 times that speed. Barry Allen would be proud. Or slightly derisive, given that he can run fast enough to rewind time. But, I digress.
The 10 rogue stars we knew about before were all transformed into rogues when a type 1a supernova hurled them away from their systems of origin. However, observations suggest that the pair traveling at ludicrous speed could only have come from a rare type of supernova in which both stars in a binary pair are whirling around one another in their final death spiral when they both explode, hurling them into space at a truly ludicrous speed. “These runaway White Dwarfs are smoking guns of double-degenerate detonations,” the study’s authors write in a preprint, available on arXiv.
Skywatchers Corner
The next few days are positively jammed with reasons to celebrate: Sunday features both a new Moon and a lunar transit, as well as Father’s Day (great for stargazing, which is also free!), while Monday is Juneteenth, and the Northern Hemisphere’s summer solstice falls this year on Wednesday, June 21. Not everyone has access to dark skies, but if you have the chance, it’s a great way to spend some low-effort quality time with your kids and/or your dad (or just the squad’s Dad Friend—you know the one, he’s got the fanny pack of cheesy crackers).
Next week, Tuesday through Thursday, the crescent Moon will be visible in an “especially lovely” celestial grouping. In the western sky shortly after sunset, the waxing crescent will glide past Mars and Venus near the blue-white star Regulus, at the heart of Leo the Lion.
Even though we’re not in a major meteor shower, most nights you can catch at least a few meteors per hour, especially under clear dark skies. So, if you can bear the mosquitoes (or somehow have enough bug repellant to keep from being exsanguinated), why not take advantage of these long summer evenings to let your eyes adjust and catch a shooting star? That’s where we’ll be. Until then, space nerds, keep your eyes on the sky, and we’ll see you next week.
[ad_2]
Source link