[ad_1]
Driven by a pandemic-related surge in virtual connectivity, an increasing number of healthcare organizations strive to accelerate their digital transformation to gain a competitive edge. Those that can effectively harness new technologies such as virtual care, data analytics, and artificial intelligence can expect to tap into $1.6 trillion in business value. Against the backdrop of a high-stakes digital race, organizations are facing exponential software growth.
This digital healthcare storm has exposed the pressing need for robust software testing strategies to ensure patient safety amidst disruption. A recent study of 55 healthcare software testing professionals and IT leaders conducted by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) sheds light on the critical testing challenges faced by healthcare IT leaders and a path to weather the digital storm.
Poor Scalability of Manual Software Testing
While automation has been widely embraced in various industries, the healthcare sector lags behind, relying heavily on manual testing methods. The study reveals that a mere 15% of healthcare providers have adopted modern test automation platforms, while a staggering 41% still rely on manual testing. This discrepancy poses significant challenges as today’s Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems become increasingly complex and customized.
How big is the problem? Of the executive leaders surveyed, only 6% were confident that they were testing enough to minimize patient risk.
Three-quarters of the providers surveyed have made concerted efforts to invest in software testing to meet the bottom line, yet nearly two-thirds report feeling inadequately resourced (including time, money, and talent) for future test requirements. The survey sheds light on the limitations of manual approaches in scalability:
- Merely 33% of manual testers are satisfied with their organizations’ capacity to scale testing to meet new requirements.
- Only 38% are satisfied with the availability of clear testing analytics
- Only 38% of manual testers believe their organizations can adequately develop test coverage across all devices and browsers.
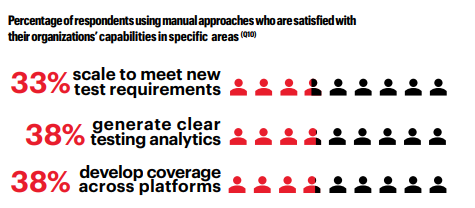
Figure 1. Percentage of respondents using manual approaches who are satisfied with their organizations’ capabilities in specific areas
The Pitfalls of A Do-It-Yourself (DIY)Software Testing Solution
While the DIY testing approach may appear attractive to over 40% of the healthcare organizations in the study, the difficulty in maintaining a robust DIY testing approach cannot be ignored.
One major challenge is the lack of technical talent required for an in-house testing solution. Modern healthcare applications and compliance requirements demand specialized expertise in programming, test automation, and test requirements. Additionally, the hidden costs associated with DIY testing, including recruiting specialized personnel and investing in infrastructure, often exceed initial budgets.
Consider EMR testing as an example: building test cases manually is an intricate task that demands deep technical expertise. This is where machine learning algorithms can augment the QA team’s capacity. By analyzing historical patterns and prioritizing test cases, ML-powered testing tools can auto-generate the most critical tests for any given platform, device, or operating system. Through the convergence of human expertise and machine learning, healthcare organizations can elevate the QA teams’ productivity and achieve broader testing coverage within time constraints.
Embracing Automated Software Testing for Resilience
Encouragingly, the study reveals that 75% of healthcare providers plan to adopt test automation within the next five years, marking a three-fold increase from the current rate. Early adopters are already experiencing the benefits, with improved resilience to future challenges. Organizations that have embraced automated software testing report higher satisfaction rates in scaling testing to meet emerging requirements.
Machine learning algorithms can play a crucial role in augmenting the capacity of software testing teams. By leveraging historical patterns and prioritizing test cases, machine learning-powered testing tools can automate critical tests across different platforms, devices, and operating systems. This convergence of human expertise and machine learning not only improves productivity but also enables comprehensive testing coverage within time constraints. For example, machine learning can streamline the intricate task of building test cases for EMR systems, allowing testers to focus on more value-added activities.
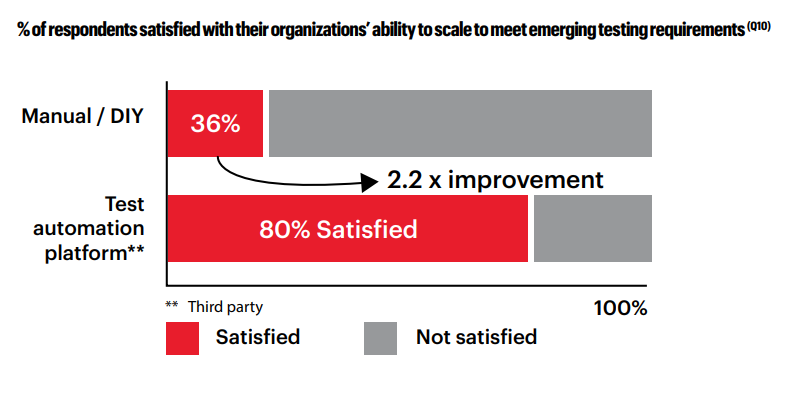
Figure 3. The percentage of respondents satisfied with their organization’s ability to scale to meet emerging testing requirements
Conclusion
The numbers don’t lie – healthcare organizations are moving into an era where healthcare software testing will become predominantly automated. Those who adopt it early stand to gain the most.
For healthcare organizations venturing into automated software testing or replacing in-house tools, staying informed about evolving healthcare testing requirements is crucial for evaluating automation vendors against critical regulatory standards. Adopting a technology-agnostic solution ensures comprehensive test coverage across all platforms and boosts efficiency. Furthermore, equipping QA teams with user-friendly test automation tools simplifies onboarding and collaboration, empowering testers to focus on strategic initiatives. By embracing automation, healthcare providers can overcome the limitations of manual testing, enhance testing coverage through machine learning, and ultimately safeguard patient well-being.
FAQ
A: Automated healthcare software testing involves using specialized tools and scripts to perform testing activities on healthcare software applications. It is rising due to the increasing complexity of healthcare systems, the need for faster and more accurate testing processes, and the demand for improved patient safety and regulatory compliance in the healthcare industry.
A: Implementing automated testing in healthcare software offers several benefits. It improves testing efficiency and reduces time-to-market for software releases. Automated tests can be repeated consistently and quickly, improving software quality. It enables the testing of complex scenarios and helps identify defects early in the development cycle. Automated testing also helps ensure compliance with regulatory standards and enhances patient safety by reducing the risk of software failures.
A: Various types of tests can be automated in healthcare software testing, including functional testing, regression testing, performance testing, security testing, and interoperability testing. Automated tests can simulate user interactions, verify data integrity, test system integration, and validate compliance with healthcare standards and regulations.
A: There are challenges to consider when implementing automated healthcare software testing. These may include the initial investment in tools and infrastructure, the need for skilled resources to develop and maintain test scripts, the complexity of healthcare systems and data, and the need for continuous adaptation to evolving software and regulatory requirements. It is important to plan and address these challenges effectively to maximize the benefits of automated testing.
A: To start with automated software testing in healthcare organizations, assess your testing needs and goals. Identify suitable tools and frameworks that align with your software development processes. Allocate resources for training and skill development. Start with small, manageable test cases or modules and gradually expand the scope of automation. Collaborate with software developers, testers, and stakeholders to establish a comprehensive automated testing strategy. Regularly evaluate and refine your automated testing processes to ensure continuous improvement.
[ad_2]
Source link