[ad_1]
NASA isn’t giving up on the Voyager spacecraft. After decades in deep space, the plucky little probe is running low on power. But NASA has devised a way to siphon energy from a backup supply, giving this iconic mission just a few more years of vital science.
Voyager 2 launched in 1977, several weeks before Voyager 1. That probe only zipped past Jupiter and Saturn in the outer solar system before heading for interstellar space. But Voyager 2 completed the “grand tour,” visiting Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune before it, too, made for the edge of known space.
Because they were destined to get as far from the sun as possible, solar panels wouldn’t have done the job. So, NASA equipped the Voyager probes with radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) similar to the technology that powers the Curiosity and Perseverance rovers. This device generates power from the heat of radioactive plutonium decay. However, the radioactive material produces less heat, and therefore less power, with each passing year. That put NASA in a tough spot. Both Voyager probes are now outside the solar system, and most of their systems are still working. As the only operational spacecraft outside the solar system, the data they return is incredibly valuable.
Previously, NASA expected the RTGs to last until 2020 or so, and power levels in 2023 are getting down there even after sacrificing non-essential systems. Luckily, there’s a little more power to be scavenged. Voyager 2 has what amounts to a surge protector, a component that monitors power levels and protects equipment from voltage fluctuations that could damage its sensitive electronics. The regulator has access to a small dedicated power flow from the RTG, and NASA has found a way to tap into that pool of extra power.
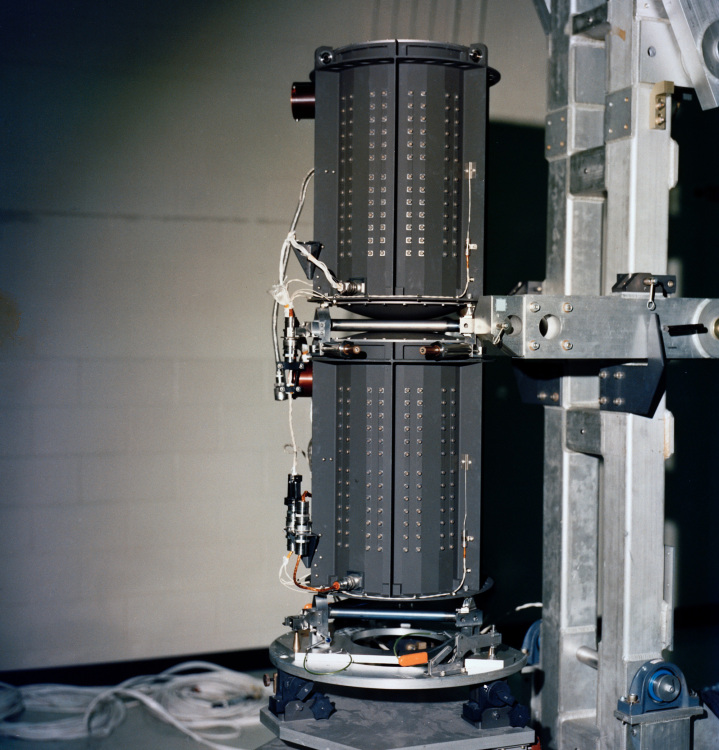
Each of NASA’s Voyager probes are equipped with three radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs), including the one shown here.
Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
According to NASA, Voyager 2’s power systems are still extremely stable after all these years, so it can get by without the voltage protection. With this additional source of power, the Voyager team estimates they will be able to keep all five of the spacecraft’s instruments online until 2026. Without this fix, the probe would have started shutting down later this year.
The Voyager engineering team is monitoring telemetry from the spacecraft to make sure its systems are stable. If successful, the team may make the same modification to Voyager 1, which left the solar system several years earlier than Voyager 2. Regardless, these missions are already an unparalleled success. NASA designed them to last four years, and they’ve already passed four decades.
[ad_2]
Source link

