[ad_1]
Hello, folks, and welcome back to This Week in Space. Virgin Galactic made its debut commercial flight, and the European Space Agency is prepping its Euclid Space Telescope for launch this weekend. But it seems like everything else is having problems, from sketchy booster stages to downed satellites, inadequate launchpads, and… well, more sketchy booster stages.
However, this week also boasts a space artichoke new diptych of Mars, courtesy of the MAVEN orbiter, plus a new photospread of Saturn and an image of a colossal cosmic filament from Webb. So we’ve got that going for us, which is nice.
European Space Agency Prepares to Launch Euclid Telescope
Europe’s much-anticipated space telescope, Euclid, is slated to launch July 1 (this Saturday) from Canaveral. When it launches, Euclid will use six ‘Korsch configuration’ mirrors to map the 3D distribution of billions of galaxies, imaging about a third of the visible universe. The mirrors, the telescope itself, and its near-infrared instruments are all made from silicon carbide, which the ESA notes is “not glass, but a ceramic only found naturally in space.”

Credit: Airbus
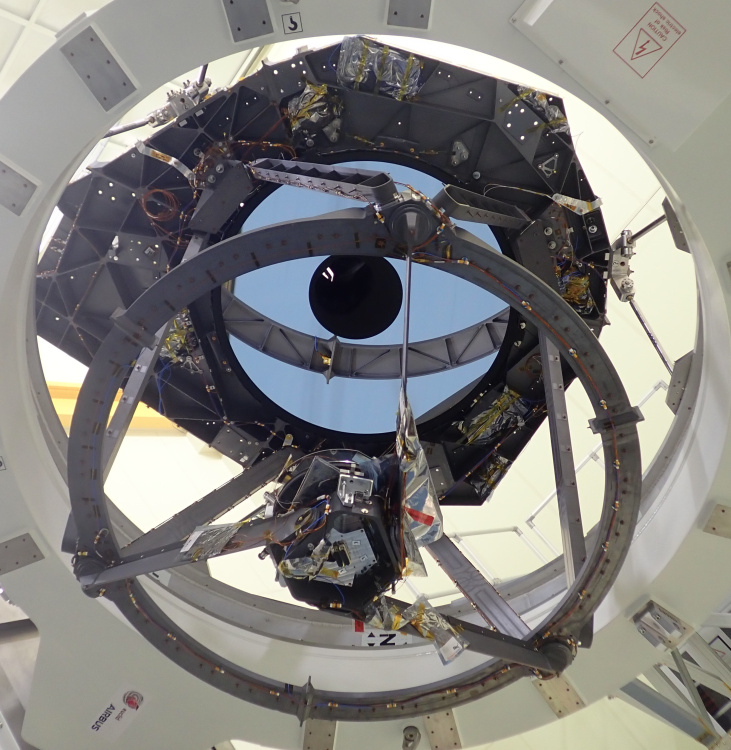
The new telescope’s instruments are so sensitive, and its mirrors must be kept so clean, that the agency requested a brand-new fairing for the SpaceX rocket that will carry it to space.
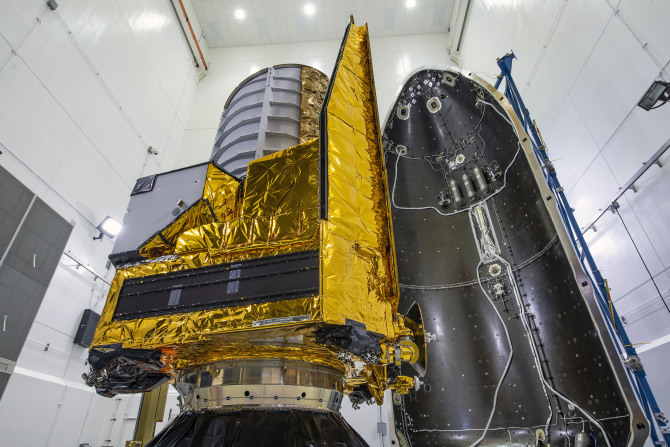

Euclid, just before techs sealed shut the brand-new SpaceX fairing.
Credit: SpaceX
NASA announced this week that its forthcoming Roman telescope (named for Nancy Grace Roman, a NASA alumna) will work with Euclid to measure the impact of dark energy more precisely. Roman, which will arrive by May 2027, will fly on SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy. But the two telescopes are rather different beasts, as shown in this image from NASA’s Goddard Flight Center:
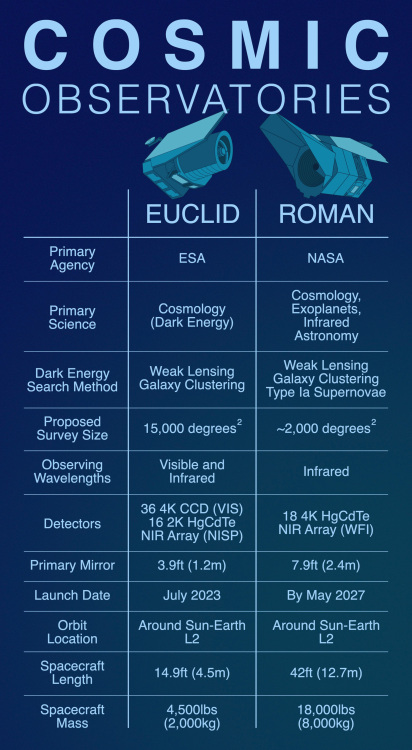
Credit: NASA Goddard
“Euclid’s first look at the broad region of sky it will survey will inform the science, analysis, and survey approach for Roman’s deeper dive,” said Mike Seiffert, a project scientist for the NASA contribution to Euclid at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“Together, Euclid and Roman will add up to much more than the sum of their parts,” said Yun Wang, a senior research scientist at Caltech/IPAC in Pasadena, California, who has led galaxy clustering science groups for both Euclid and Roman. “Combining their observations will give astronomers a better sense of what’s actually going on in the universe.”
Virgin Galactic Aces First Commercial Flight
Thursday, Virgin Galactic made a successful first commercial flight of its VSS Unity, a rocket-powered spaceplane the company will use in its commercial launch services. The mission, dubbed Galactic 01, launched Thursday morning from Spaceport America. The crew included pilot Mike Masucci, copilot Nicola Pecile, and astronaut instructor Colin Bennet, all from Virgin Galactic, as well as Pantaleone Carlucci of CNR Italy, Col. Walter Villadei, and Lt. Col. Dr. Angelo Landolfi (the latter two from the Italian Air Force).
Last Ariane 5 Flight Is Scheduled for Next Week
Arianespace has announced that the last Ariane 5 rocket will take flight on July 4. After more than two years of delays, the mission was originally scheduled for June 16. However, problems with the rocket’s pyrotechnic transmission lines forced a further delay.
Designated VA261, the flight will launch from French Guiana during a two-hour launch window Tuesday evening, local time. The swan-song mission will deliver two satellites, the Heinrich-Hertz and Syracuse 4B, into a geostationary transfer orbit.
Meanwhile, ArianeGroup (of which Arianespace is a subsidiary) announced a successful test fire of its reusable Prometheus rocket. The rocket, which can deliver some 100 metric tons of thrust, is to serve as the backbone of a fleet of workhorse rockets that it hopes will enter service sometime in the 2030s.
“Our firing was a crucial milestone on the journey to an operational product with all the test objectives in terms of operating points and duration achieved,” said Jérôme Breteau, head of future space transportation systems at the ESA. “Further activities are planned to improve and complete the engine. For example, the engine configuration did not incorporate nozzle extension, and some combustion element manufacturing technologies being developed in parallel are not yet completed.”
ULA Ships Vulcan Centaur Back to Factory to Shore Up Fuel Tank
On March 29 of this year, United Launch Alliance suffered a disastrous vehicle loss in an explosion during a structural test of its Centaur rocket’s upper stage. Taking no chances, after a three-month investigation, ULA techs determined that the upper stage already mounted to the first flight-rated Vulcan rocket wasn’t flightworthy. Instead, citing the need for reinforcements to the upper stage’s steel fuel tank, ULA will take the partially assembled rocket apart and ship the upper stage back to its factory.
After the March 29 explosion, the Vulcan Centaur simply won’t launch this summer. However, ULA spokespeople aren’t ruling out a launch within 2023.
SpaceX Making ‘Well Over 1,000’ Adjustments to Starship Before Next Launch
According to a discussion between journalist Ashlee Vance and Elon Musk, SpaceX has made over a thousand changes to Starship following its test flight back in April. While that first test was successful as far as getting Starship off the ground, igniting the booster stack’s 33 Raptor engines did significant damage to the launchpad. An attempt to detonate the rocket following its post-launch malfunction was also unusually delayed. While the rocket was eventually destroyed by its onboard self-destruct, the process took longer than expected.
“There are really a tremendous number of changes between the last Starship flight and this one, well over a thousand,” said Musk. “I think the probability of this next flight working, getting to orbit, is much higher than the last one. Maybe it’s like 60 percent. It depends on how well we do at stage separation.”
My colleague Ryan Whitwam noted that future Starship designs will use so-called ‘hot staging’ to boost Starship’s deliverable payload by roughly 10 percent. A rocket that uses hot staging ignites its upper stage while still connected to the booster. The Russian Soyuz uses hot staging, but current US launch vehicles do not. US-designed rockets typically exhaust their first stages before the second stage separates from the rest of the rocket. Once the separation is complete, the second stage engine activates. This simplifies rocket design, since otherwise the top of the first stage has to be capable of withstanding the second stage’s engine burn. The advantage of hot staging is that it increases a rocket’s total throw weight to orbit.
Other features highlighted by Musk include a steel-reinforced concrete pad with water channels for cooling during launch, new vents at the top of the booster, new manifolds on the Raptor engines to reduce gas leaking into places where it isn’t wanted, electronic thrust vector controls, and better shielding around the Raptor engines themselves.
SpaceX hopes to be ready to launch the next Starship test flight within six weeks, but whether that happens will ultimately be up to the FAA.
South Korea Fishes North Korea’s First Spy Satellite Out of Ocean
On May 31, North Korea’s first spy satellite, dubbed Malligyong-1 (Telescope-1), crashed into the ocean following an early ignition of its second stage. The satellite was carried by North Korea’s Chollima-1 rocket. According to 38North.org, the Chollima-1 is believed to be based on the Hwasong-17 ICBM, but with a second and third stage optimized for space launch. This was Chollima-1’s debut, and the launch vehicle didn’t exactly cover itself in glory.

Credit: South Korean Defense Ministry via Getty Images
Per South Korea’s Yonhap News Agency, efforts to retrieve the satellite and its launch vehicle are continuing, but at least part of the Malligyong-1 was recovered on June 26. Some fuselage from the rocket was salvaged back on June 15, but the satellite itself had eluded searchers until this week. 38North reports that the cause of the initial failure was attributed to “the low reliability and stability of the new-type engine system applied to carrier rocket ‘Chollima-1’ and the unstable character of the fuel used.”
According to the North Korean National Aerospace Development Administration (aka NADA), it will undertake a thorough investigation of the failure and take whatever actions are required to enable a second, hopefully successful launch as quickly as possible. Both South Korea and the United States are prime targets for North Korea’s spy satellite program, but the Hermit Kingdom has announced a number of other uses for its nascent satellite program, including a desire for better weather forecasting, better communication services, and a future North Korean state propaganda agency-approved compilation of high-res Earth photography titled “Oh the Places You Won’t Go.”
It’s Not Pee Anymore, We Promise: Dispatches From the International Space Station
Thursday afternoon, a SpaceX Cargo Dragon cast off from the International Space Station. The capsule launched June 5 from the Kennedy Space Center bearing the usual tonnage of supplies, in addition to two new roll-out solar arrays, and it will make a parachute-assisted splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean sometime today.

Credit: NASA TV
While the Dragon capsule was docked with the station, astronauts aboard celebrated an achievement not for the squeamish: peak urine recycling. (Peak pee-cycling? No? I’ll see myself out.) Normally, a vacuum distillation system lets ISS personnel reclaim some 93-94% of the water from their breath, sweat, and urine. This leaves behind a highly concentrated brine that still contains reclaimable water. But with the addition of a brine processing system, that figure has hit the long-sought milestone of 98% reclamation.
Jill Williamson, ECLSS water subsystems manager, reassured readers in a blog post, pointing out very patiently that the reclaimed water is “far superior” to municipal tap water. “The processing is fundamentally similar to some terrestrial water distribution systems, just done in microgravity,” Williamson said. “The crew is not drinking urine; they are drinking water that has been reclaimed, filtered, and cleaned such that it is cleaner than what we drink here on Earth. We have a lot of processes in place and a lot of ground testing to provide confidence that we are producing clean, potable water.”
Between the confined spaces and the hazards of radiation, long-term microgravity, and the vacuum of space, it’s no wonder NASA requires that prospective astronauts be of steely disposition. Listen, when the best news coming off the ISS is “Hooray, we can drink an ever-increasing fraction of our pee,” you know these people have to be going through it.
Orion Heat Shield Installed for Artemis II Mission
Sunday, technicians at the Kennedy Space Center finished installing the heat shield that will protect the Orion capsule during the Artemis II mission. The 16.5-foot-wide heat shield is one of the most important systems on the Orion spacecraft ensuring a safe return of the astronauts on board. As the spacecraft returns to Earth following its mission around the Moon, it will be traveling at speeds of about 25,000 mph and experience outside temperatures of nearly 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Inside the spacecraft, however, astronauts will experience a much more comfortable temperature in the mid-70s thanks to Orion’s thermal protection system.
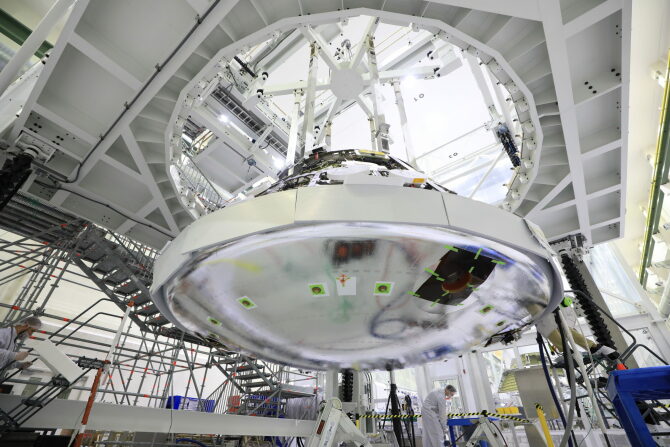

Credit: NASA/Cory Huston
The spacecraft will be outfitted with some of its external panels ahead of acoustic testing later this summer, as part of “shake, rattle, and roll” testing to make sure that Orion can handle the vibration it will experience during its mission. Then, technicians will attach the crew module to Orion’s service module.
Last Call: NASA Seeking Ideas for Artemis III
Earlier this month, NASA announced that it was looking for ideas for astronaut-deployable experiments, to take advantage of the unique location of the Artemis III landing. The mission will touch down within 6 degrees of the moon’s south pole, which has remained untouched despite people and robots scuffling around on the moon for decades.
Even if you miss this week’s deadline, the agency will still be looking for ways to get the most science out of Artemis IV and later missions.
MAVEN Orbiter Captures Martian Ozone Layer in New Diptych
NASA released a new colorized composite image showing two separate views of Mars. At left, you can see the planet as it appeared in July of 2022, with clouds visible in its southern hemisphere. But at right—well, it might not be an actual space artichoke, but if you cross your eyes, it kind of looks like one.

Credit: NASA/Maven
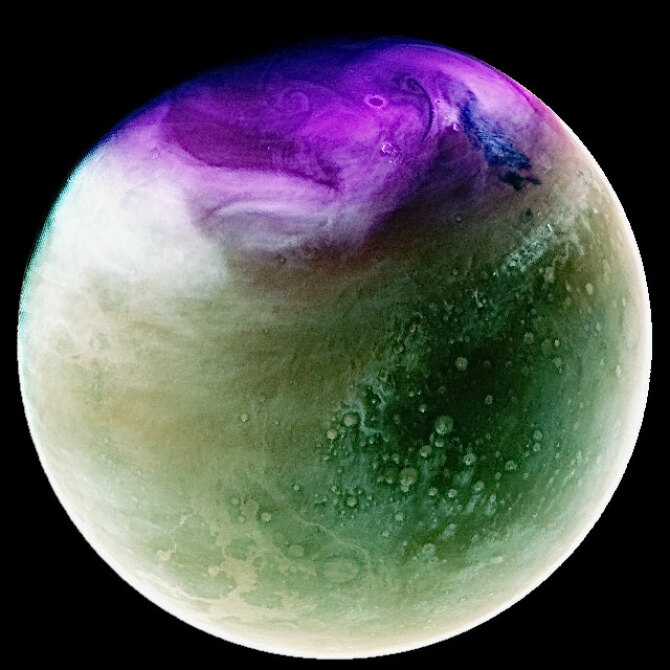

Credit: NASA/MAVEN
The magenta in the latter image, taken in January of 2023, shows off where ozone collects during the Martian spring.
Perseverance Shows Twice the MOXIE
As tantalizing a target as Mars is for manned space exploration, the Red Planet has some downsides would-be visitors must overcome. Chief among these is its general lack of concern for the life support requirements of humans, including breathable air.
Perseverance’s MOXIE—short for “Mars Oxygen In Situ Resource Utilization Experiment”—was charged with discovering if it was possible to produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. While the experiment has already been demonstrated to work, NASA announced this week that it had produced 12 grams of oxygen per hour: double the initial scientific target.
Nobody Tell Homer: Percy Spots a Meteoric Donut
In other Perseverance-related news, the rover made headlines this week when it spotted what may be a donut-shaped meteorite. While this isn’t the first meteor that Perseverance and its older sibling, Curiosity, have found, any information NASA can gather from the object will expand our understanding of how Mars has been shaped by various impactors.

Credit: NASA/SETI
While taking the photo, Perseverance also took the opportunity to zap this particular rock to sample its composition, but NASA hasn’t released any results from that test yet. Whether it’s a relative newcomer or a deep time remnant, rocks we find on other planets could tell us as much or more about the formation of the solar system as the meteorites we find on Earth.
New NASA-Approved LEGO Models of Perseverance, Ingenuity
A new LEGO Technic building set developed in cooperation with NASA’s JPL aims to make teaching about space more fun, starting with the Perseverance Mars rover—and its companion helicopter Ingenuity, the little space copter that could. According to NASA, the kit is “designed to spark kids’ interest in engineering and space via traditional toys and augmented reality.” The new LEGO kit is based on the real rover and helicopter, which have been exploring Mars’ Jezero Crater since landing there more than two years ago.
Mars Dune Alpha Experiment Begins
The four volunteers who will spend their next year inside Mars Dune Alpha, NASA’s simulated Mars environment, have officially entered the habitat and closed the door behind them. Ryan has more on the experiment, and the four pseudo-astronauts whose efforts will hopefully inform future Mars expeditions.
First Raw Webb Telescope Images of Saturn Have Arrived
The JWST Feed website exists solely to publish every scrap of data received by Webb as soon as it’s released—and right now, that’s a whole ton of new views of Saturn. The images haven’t been processed yet, but you can see our preview of the Saturn photospread here.
Antarctic IceCube Detector Images Galaxy With Neutrinos
Scientists from the IceCube Neutrino Observatory have used machine learning to produce the first map of the Milky Way based not on photons, but on the galaxy’s neutrino emissions.

Credit: IceCube/NSF
The IceCube observatory is a network of sensors embedded throughout a cubic kilometer of pristine Antarctic ice. Neutrinos interact only rarely with matter, but when they do, they release tiny flashes of light. IceCube collaborators used machine-learning analyses that selected for “cascade” events (neutrino interactions in the ice that result in roughly spherical showers of light), to reduce ‘contamination’ by neutrinos and muons originating from cosmic-ray interactions with the atmosphere. Ultimately, the team said at a press event, the “higher purity” of the cascade events gave a better sensitivity to astrophysical neutrinos from the southern sky, yielding a panoramic map of neutrino sources from along the galactic plane.
“I remember saying, ‘At this point in human history, we’re the first ones to see our galaxy in anything other than light,'” said Drexel University physicist Naoko Kurahashi Neilson, recalling the moment she and coauthors Steve Sclafani and Mirco Hünnefeld (with Drexel and TU Dortmund University in Germany, respectively) first saw the image.
“As is so often the case, significant breakthroughs in science are enabled by advances in technology,” said Denise Caldwell, director of NSF’s Physics Division, in a statement. “The capabilities provided by the highly sensitive IceCube detector, coupled with new data analysis tools, have given us an entirely new view of our galaxy—one that had only been hinted at before. As these capabilities continue to be refined, we can look forward to watching this picture emerge with ever-increasing resolution, potentially revealing hidden features of our galaxy never before seen by humanity.” The work appears in Thursday’s issue of Science.
Astronomers Trace Ancient Filament of ‘Cosmic Web’ Anchored By Quasar
Woven throughout the universe, there is a structure of bewildering scale, an enormous mesh of filaments (themselves made of dozens of galaxies) collectively called the ‘cosmic web.’ Appropriately, astronomers using the Webb telescope have discovered an early strand within this cosmic structure: a long, narrow filament of 10 galaxies that existed just 830 million years after the Big Bang. The filament is three million light-years long, but the astronomers report that the whole thing is anchored by a quasar—a luminous active galactic nucleus, powered by a supermassive black hole at its core. Eventually, the team believes, the filament will evolve into a massive cluster of galaxies.

Credit: Image: NASA, ESA, CSA, Feige Wang (University of Arizona); image processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
The discovery is from the ASPIRE project (A SPectroscopic survey of biased halos In the Reionization Era), which studies the “cosmic environments” of the earliest black holes. In total, the program will cast its telescopes’ gaze upon 25 quasars, all of which existed within the first billion years after the Big Bang.
NANOGrav Project Detects ‘Nanohertz’ Gravitational Waves Too Big for LIGO to See
Using ultra-precise measurements of the fluctuation of pulsars, the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) group reported this week that it has detected so-called ‘nanohertz’ gravitational waves. These ultra-long-wavelength disturbances in spacetime emanate from supermassive black holes—and they’re simply too huge for LIGO to see.
Skywatchers Corner
Skies are hazy across much of the nation this week, owing to storms and another blast of smoke from the Canadian wildfires. Unfortunately, this makes it difficult to see things like the Milky Way, which (for those with dark skies) is visible toward the south as soon as it’s dark. Nevertheless, early July offers much to skywatchers.
The next full Moon will appear on Monday morning (July 3), and it will seem full for up to three days. For Americans, this lines up really nicely with the timing of Independence Day celebrations, which often include fireworks beginning shortly after nightfall on July 4. If you’re going to see fireworks, the juxtaposition of the Moon and the glowing fireworks will be a striking view—and a lovely photography challenge.
See you next week!
[ad_2]
Source link

