[ad_1]
Hello, readers, and welcome back to This Week in Space. Happy Spring!
Did you ever wonder what you’d get if you crossed Tatooine and Jupiter? Neither did we. But this week, we’ve got reports of sandstorms on a gas giant, a rocket launch that failed successfully, and some genuinely wild solar weather. Scientists also debuted a new and much stronger version of concrete that definitely doesn’t contain human blood. And for those who love it when academics get mad, we’ve got a new, anticlimactic explanation for ‘Oumuamua’s weird orbit. Plus, Russia hasn’t been paying its bills, and the repo man cometh.
It’s Your Move, Mr. Putin: Kazakhstan Seizes Russian Space Assets
The Soviet Union built the Baikonur Cosmodrome in 1955 as an ICBM launch site. Eventually, with the launch of Sputnik and Vostok 1, the cosmodrome expanded into the world’s first spaceport—and a crucial pillar supporting Soviet access to space.
When the Soviet Union dissolved, drawing the new maps presented another problem for Russia. Baikonur fell within the newly formed nation of Kazakhstan. Russian officials ground their teeth and signed an agreement with Kazakhstan, giving Russia access to Baikonur through the year 2050 in exchange for about $100 million a year.
Russia would understandably prefer to have its launch facilities on sovereign soil. To that end, it has been spending (and losing) a lot of money building a new spaceport called Vostochny. But the country’s space corporation, Roscosmos, has also been working on a new medium-capacity rocket, Soyuz-5, that it expects to launch from Baikonur. Meanwhile, Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has rapidly drawn down the nation’s remaining bank balances. As a consequence, it hasn’t been paying all its bills. Ars Technica reports that the Republic of Kazakhstan has “seized the property of TsENKI, the Center for Utilization of Ground-based Space Infrastructure, in Kazakhstan. This firm, a subsidiary of Roscosmos, is responsible for launch pads and ground support equipment for the Russian space corporation.” According to the report, TsENKI is forbidden from removing “any assets or materials” from Kazakhstan.
Play stupid games, win stupid prizes.
Good Luck, Had Fun: Terran 1 Launch Failed Successfully
Relativity Space launched its 3D-printed, methane-fueled Terran 1 rocket Wednesday night. The first stage fired as expected, but the second didn’t follow suit. Relativity hasn’t given an official cause yet. However, they did post a statement on Twitter. We’re making a note here: huge success.
Now that Terran 1 has taken off, Relativity’s next move will be to analyze data from the flight. What it learns may inform the company’s movement on its larger Terran R lift vehicle.
Researchers Discover Uracil, Vitamin B3 in Samples From Ryugu
Researchers have analyzed samples from asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the monomer “informational units” that make up RNA, a polymer nucleic acid. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, was also detected in the same samples.
Without getting too breathless about it, uracil is one of the nucleobases found in RNA. (It’s the one that replaces thymine after transcription from DNA to RNA, to be specific.) When chained together, nucleobases make up nucleic acids like DNA; that’s true enough. And niacin is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms. But listen. These molecules are not nearly as special as they sound. This is what uracil looks like:
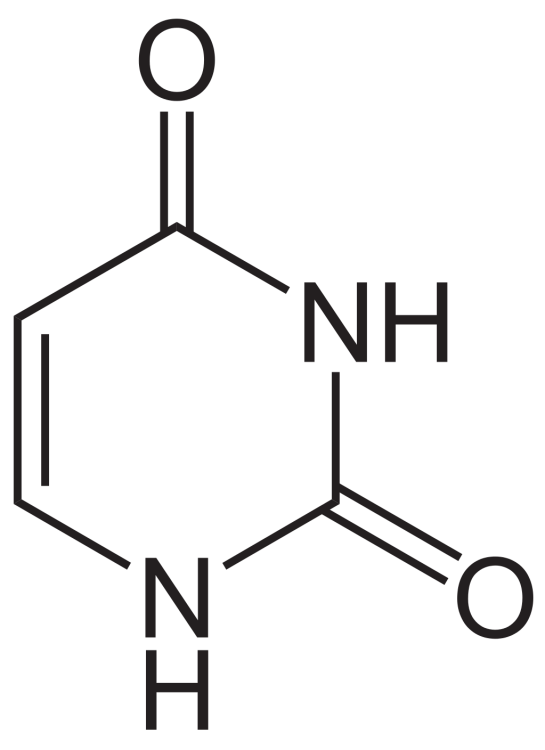
I have just had it with the phrase ‘the building blocks of life.’ THIS MOLECULE IS PLANAR.
Credit: Public Domain
This is literally just a dirty benzene ring with a couple of oxygen atoms tacked on. Life, it ain’t. Here on Earth, it comes from lightning or UV rays (sunlight) striking ocean water.
But molecules like this do tell us some valuable things. For context, those exposed oxygen atoms mean uracil is water soluble. That confirms prior telescope observations and spectra suggesting Ryugu was mostly water ice. Cross-checking our work makes us more confident in our models of what’s going on offworld.
UAE Astronaut Observes Ramadan in Space
Sultan Al-Neyadi is the first astronaut from the United Arab Emirates to fly a six-month mission aboard the International Space Station. An observant Muslim, Al-Neyadi faces unique challenges in keeping his faith during the Crew-6 flight. How do you observe Ramadan in space? Carefully.
During the Islamic holy month of Ramadan, most adult Muslims fast from sunrise to sunset. Observing Ramadan is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. However, as a traveler (far from home indeed!), Islamic rules permit Al-Neyadi to eat normally during his six-month stay in orbit. Moreover, seeing a sunrise every ninety minutes would complicate even the most devout astronaut’s daily prayers.
Practical scholars of the faith concluded some years ago that observant Muslims in orbit should keep the faith in their hearts, following the rules and etiquette of Islam as they can. At a conference before takeoff, Al-Neyadi confirmed that the mission schedule might not allow normal Ramadan fasting, but he’s not feeling an internal conflict. If the schedule allows, Al-Neyadi said in livestreamed remarks from Houston that he may still try to fast on some days. But he doesn’t feel pressed to do anything “that can jeopardize the mission or maybe put the crewmember in a risk.”
“We’ll see how it goes,” he said.
New TOLIMAN Mission Will Hunt for Habitable Planets at Alpha Centauri
Speaking of Islamic contributions to space: A new, pint-sized space telescope with an ancient name will launch in 2027 to search Alpha Centauri for habitable planets.
The telescope’s name is TOLIMAN, en homage to Toliman, the name for Alpha Centauri in Arabic during the golden age of Islamic astronomy. TOLIMAN stands for ‘the Telescope for Orbit Locus Interferometric Monitoring of our Astronomical Neighbourhood.’ The University of Sydney recently signed a contract with EnduroSat for launch services.
Once it’s in the sky, TOLIMAN will peer closely at the Alpha Centauri system, checking for exoplanets using the “wobble” method (as opposed to the “transit” approach). Planets tug on the stars they orbit, moving them a tiny bit in the sky. Astronomers will use TOLIMAN to watch Alpha Centauri for these little “wobbles,” hoping to find what the transit method struggles to see: an exoplanet that isn’t orbiting perfectly edge-on between us and its star.
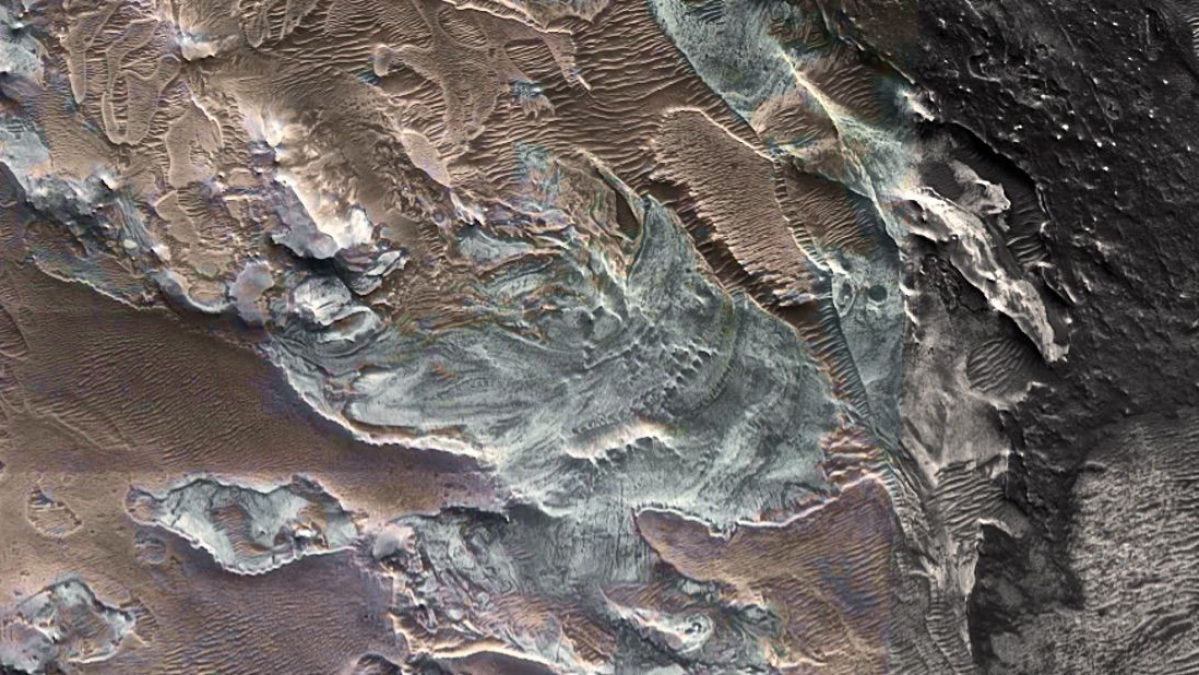
‘Relict Glacier’ on Mars’ Equator Rekindles Hopes of Buried Water Ice
At the 54th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, researchers reported that a bright spot near Mars’ equator was a ‘relict glacier.’ What the scientists found isn’t the glacier itself—it’s the negative space formed when a glacier of water ice sublimated out from within a salt deposit. But it hints that useful quantities of water ice might still be buried under the surface at higher latitudes.
“Water ice is, at present, not stable at the very surface of Mars near the equator at these elevations. So, it’s not surprising that we’re not detecting any water ice at the surface. It is possible that all the glacier’s water ice has sublimated away by now. But there’s also a chance that some of it might still be protected at shallow depth under the sulfate salts,” explained lead author Dr. Pascal Lee of the SETI Institute.

Credit: NASA/SETI
What led Lee and coauthors to conclude that there was a glacier here instead of just some light-colored rock? There are places here on Earth where a thick layer of sulfate salts has sheltered a mass of ice underneath it. According to the authors, the Altiplano Flats in South America contain just such deposits of sulfate salts, a thick layer of pale crystals called salars above ancient glacial ice. Shielded from the sunlight and held down by the pressure, the authors say, this ancient ice neither melts nor sublimates away.
New NASA, ESA Tools Show Mars’ Jezero Crater Like Never Before
Perseverance and Ingenuity are still—still!—just truckin’ right along on Mars. Ingenuity is still flying. And thanks to a new map widget and a new video flyover, we can see better than ever what our rovers and satellites see when they look at Mars.
Scientists sent Perseverance and Ingenuity to Mars to explore a particular spot in a big Martian crater. It looks for all the world like the wall of the crater gave, releasing an influx of mud, silt, and stones. Clay deposits in the crater floor suggest it was once full of liquid water, perhaps forming a crater lake. You can check out the area’s topography with this zoomable map widget, courtesy of the European Space Association.
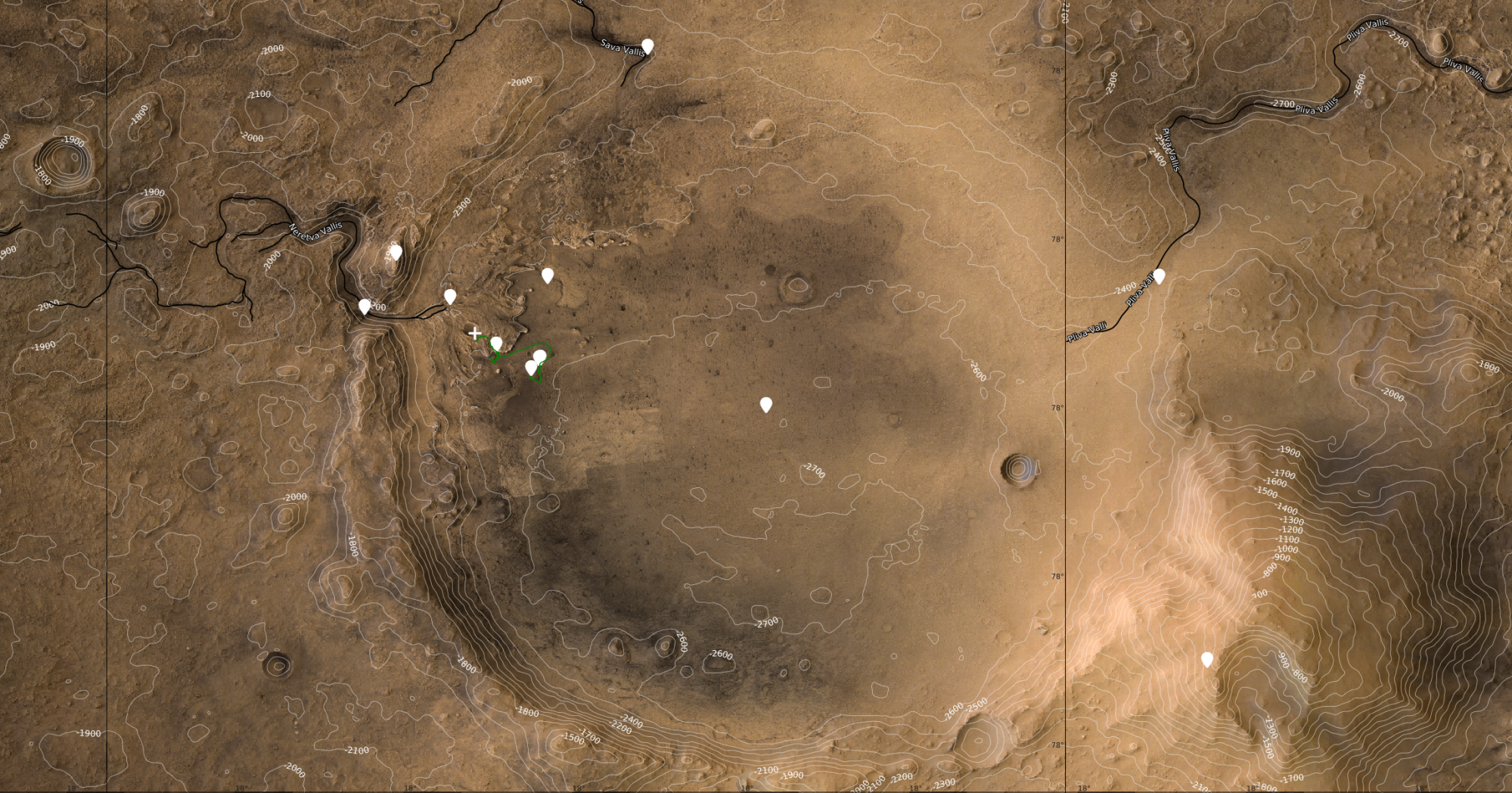
Sure does look like a mudslide into a crater.
Credit: NASA
For a different perspective, you can also check out this flythrough of Jezero Crater, courtesy of NASA.
Taikonauts Grow Rice In Microgravity
The Chinese Academy of Sciences announced this week that Chinese taikonauts have successfully grown and harvested rice seeds aboard the country’s Tiangong space station. Now that the seed samples are back on Earth, Chinese researchers will plant the seeds to see how healthy they are as part of the end phase of the Shenzhou-14 mission to Tiangong.
The cultivation of rice, China’s staple crop, in space is part of a larger push by the Chinese space program toward a presence on the Moon. Integral to that plan is the upcoming Chang’e-7 rover. China intends to send the rover to the lunar south pole in 2026 in search of water ice and other resources—just like NASA’s upcoming VIPER moon rover. The Chinese National Space Administration hopes to break ground on a lunar settlement by 2028.
While making our space menu, we’ll need a salad to go with all that rice. From the University of Adelaide comes a new “space salad” designed to keep space travelers healthy on long missions.
The salad has seven ingredients: soybeans, poppy seeds, barley, kale, peanuts, sunflower seeds, and sweet potatoes. All of the plants can grow in small spaces, and now we know they do fine in microgravity, too.
Astronomers Find Sand Clouds on a Gas Giant
Researchers observing with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have pinpointed “silicate cloud features” in the atmosphere of a relatively nearby exoplanet. A gas giant, its atmosphere churns so wildly that NASA called it “the most variable planetary-mass object known to date.”
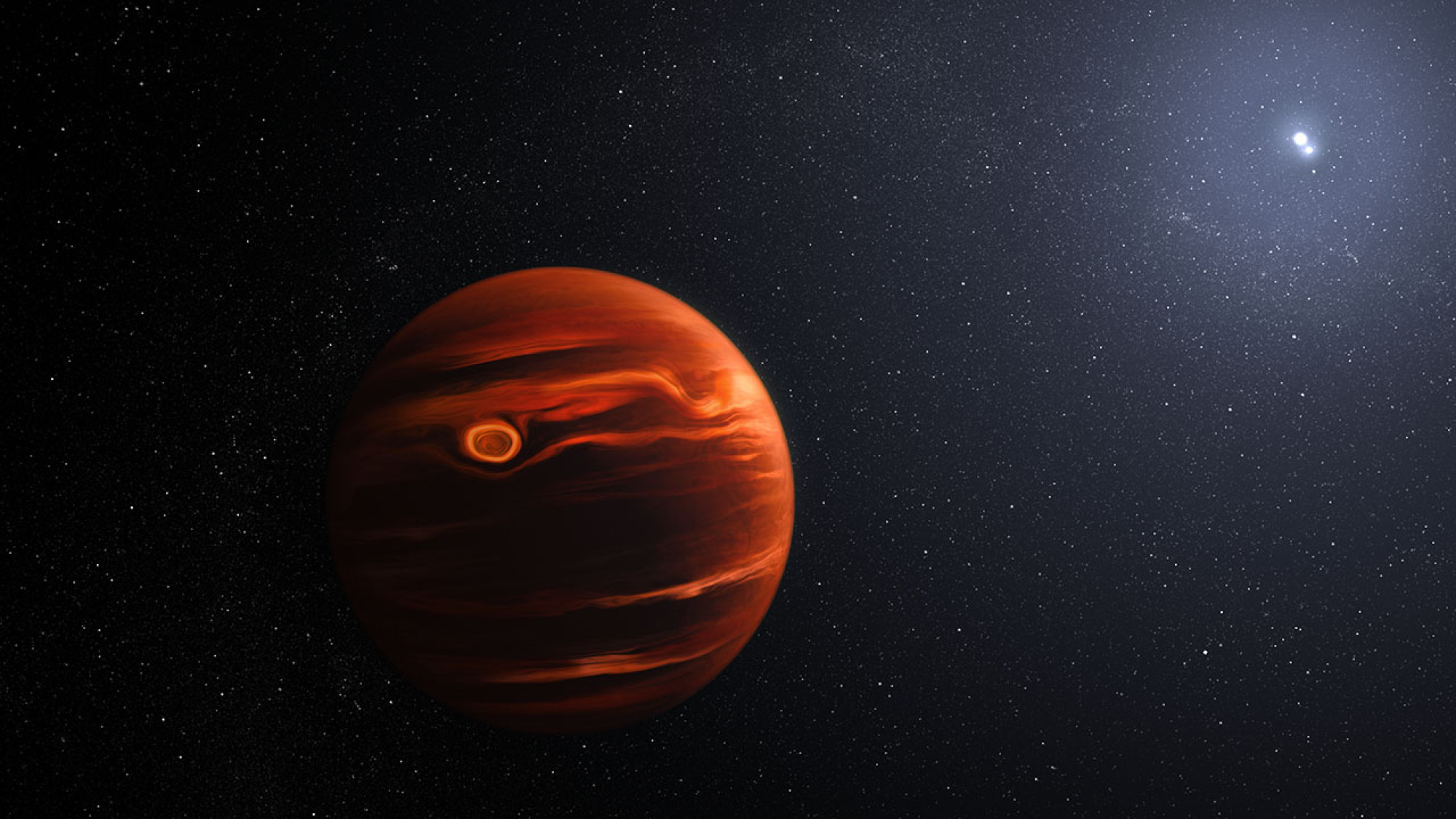

Artist’s illustration of VHS 1256 b.
Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Cataloged as VHS 1256 b, the angry-sand-colored planet is about 40 light-years away. And, perhaps appropriately, it orbits two stars over a 10,000-year period. “VHS 1256 b is about four times farther from its stars than Pluto is from our Sun, which makes it a great target for Webb,” said team lead Brittany Miles of the University of Arizona. “That means the planet’s light is not mixed with light from its stars.”
Up in its atmosphere, where the silicate clouds roil and churn, temperatures reach a scorching 1,500 degrees Fahrenheit (830 degrees Celsius). It’s not quite hot enough to be raining molten glass—it’s just the worst sandstorm ever. “The finer silicate grains in its atmosphere may be more like tiny particles in smoke,” noted co-author Beth Biller of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland. “The larger grains might be more like very hot, very small sand particles.”
Somehow, what you get when you cross Jupiter and Tatooine is worse than the sum of its parts.
Scientists Debut Extra-Strong ‘Starcrete’ That Definitely Doesn’t Contain Human Blood
Researchers have announced a new type of extra-strong concrete they hope will be useful for building structures offworld. It’s made of regolith and reinforced with gelatinized potato starch, which made no sense until I remembered it’s possible to make a chef’s knife out of Jello. The authors report that the new material, which they’ve dubbed ‘Starcrete’ (for ‘starch’ and ‘concrete’), was much stronger than other types of reinforced concrete under flexion and compression. And—because they had to specify—it does not contain human blood. Unlike previous versions. Which did.
The recent research builds on prior work by the same team, exploring a variety of more and less horrifying concrete additives, including but not limited to human urine, saliva, and blood (or cows’ blood plasma, not that that’s better). In that study, the authors also looked at the role of magnesium chloride as a concrete additive, including ways to source the chemical offworld. Did you know there’s magnesium chloride in human tears? Now you do.
In a statement, lead author Aled Roberts conceded that potato-crete would probably make for a better living experience than bricks literally made from our precious bodily fluids. “Astronauts probably don’t want to be living in houses made from scabs and urine,” he said.

Lead author Aled Roberts. If you were going for mad scientist, my guy, you nailed it.
Credit: University of Manchester
Please accept the following image of the conjunction between Jupiter and Venus from earlier this month as compensation for having just made you read that. If it makes you feel any better, I had to write it.
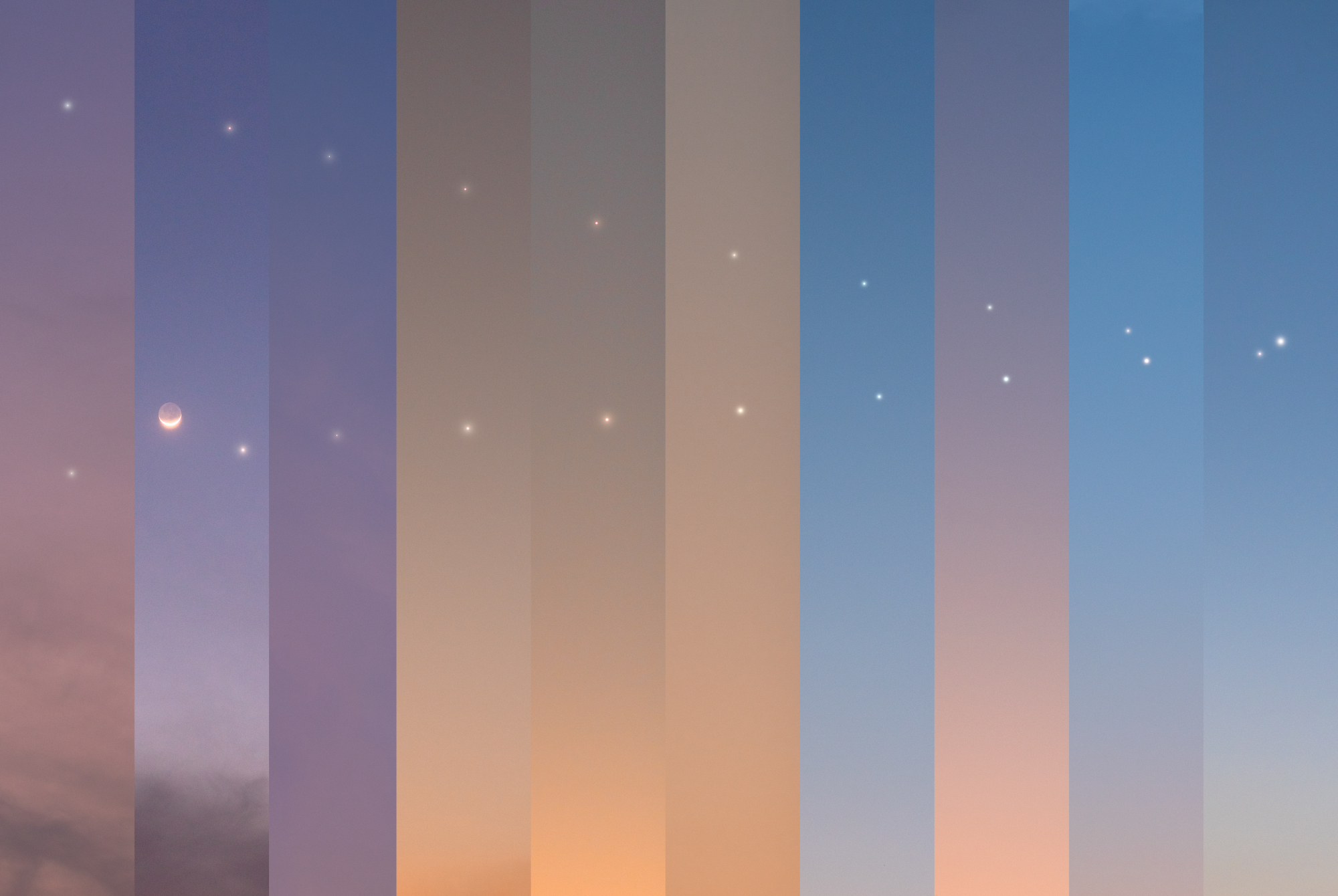

Ahhh, eyebleach.
Credit: Soumyadeep Mukherjee, via NASA
A Simple Explanation for ‘Oumuamua’s Weird Acceleration
A few years ago, we found the first confirmed object from outside our solar system: a cigar-shaped chunk of something, hurtling in at an angle and speed we’d never seen. Astronomers named it ‘Oumuamua, Hawaiian for “messenger from afar, arriving first.” It left as quickly as it came, speeding up as it moved away from the Sun—much more quickly than gravity alone could ‘slingshot’ it away.
How could this be? At the time, Harvard astronomer Avi Loeb and coauthor Shmuel Bialy contended that the best explanation was that ‘Oumuamua was a ship of alien manufacture, using solar sails to accelerate. However, a far simpler explanation may be responsible for what we see. Astrochemist Jennifer Bergner and coauthor Darryl Seligman have proposed that ‘Oumuamua might be just a great big shard of porous water ice, off-gassing molecular hydrogen on its sunward side. Such a tiny force wouldn’t carry away dust still embedded in the ice matrix. This could account for the fact that ‘Oumuamua didn’t have a tail like comets usually do.
“What’s beautiful about Jenny’s idea is that it’s exactly what should happen to interstellar comets,” Seligman said. “We had all these stupid ideas, like hydrogen icebergs and other crazy things, and it’s just the most generic explanation.”
Loeb, for his part, is staying on topic. “The authors of the new paper claim that it was a water ice comet even though we did not see the cometary tail,” Loeb said, according to The New York Times. “This is like saying an elephant is a zebra without stripes.”
Bergner and Seligman will publish their report in this week’s issue of Nature.
Skywatchers Corner: Solar Weather
Spring has sprung for folks north of the equator, and with spring comes the dawn of spring allergy season. For many cultures, the spring equinox also brings an important holiday. Such is the case in Islam; the holy lunar month of Ramadan began Wednesday evening, with the first sliver of the first crescent Moon rising after the equinox. Christian liturgical calendars also use the moon phases and the equinox to determine where Easter will fall during any given year. (It’s April 9 this year.)
Sungazing is mainly the province of satellites because looking directly at the sun (even during an eclipse) can burn our eyes. However, this week we’ve seen a remarkable escalation of solar activity, as if the sun itself was celebrating its return after the long nights of winter. A gigantic hole opened up in the sun’s atmosphere earlier this week, producing a stream of high-energy particles that thankfully struck us with just a glancing blow. And I mean gigantic: The hole was dozens of times wider than our entire planet.
From yesterday well into this evening, the associated geomagnetic storm is still lighting up skies worldwide, bringing the aurora borealis as far south as Seattle and upstate New York.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory also captured an equally gigantic tornado elsewhere on the sun. Just before the coronal hole opened up, the SDO and other observers captured a twisting filament of plasma near the sun’s north pole—a “sun devil” nearly 75,000 miles long.
Back here on Earth, things are much more sedate. This evening after sunset, look westward to see Venus shining bright, just below the crescent Moon. Tomorrow night, the crescent Moon will sit next to the Pleiades.
That’s all for this week. But keep your eyes peeled—next week, we’ll be treated to another “planetary parade,” featuring five planets within about 45 degrees in the sky. See you then!
[ad_2]
Source link

